
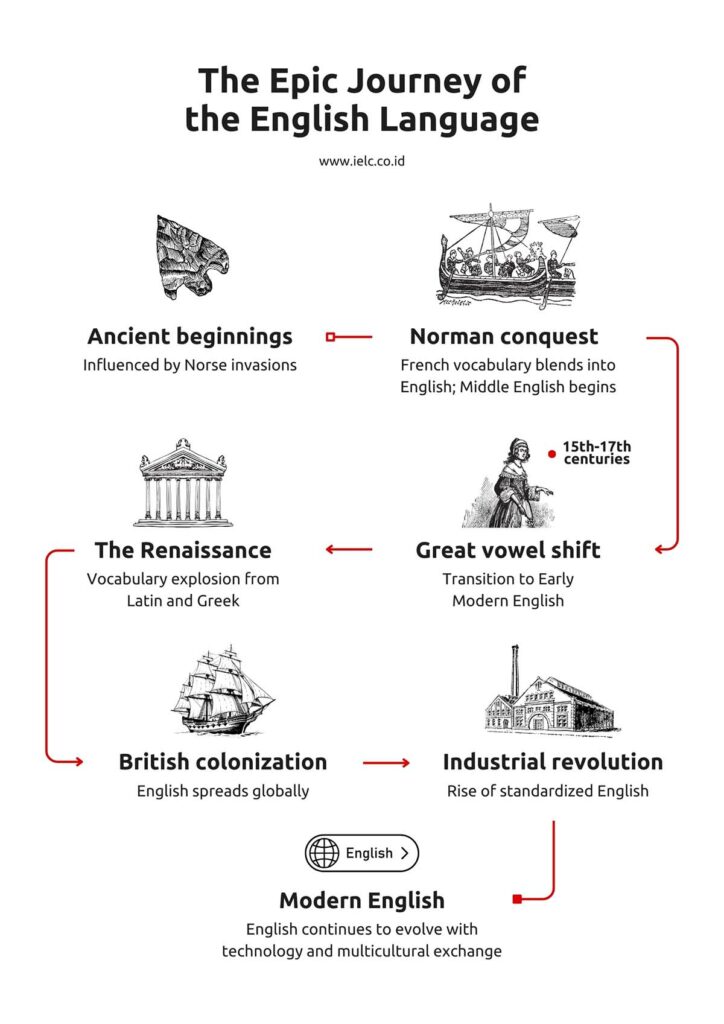
The history of English: from old to modern in a nutshell
Welcome, English learners and curious minds alike!
Today, we’ll embark on a fascinating journey through time, tracing the rich tapestry of the English language from its humble beginnings to its current status as a global lingua franca!
The story of English is not just a tale of words and grammar; it’s a saga of invasions, cultural transformations, and the unyielding spirit of a language that refused to be confined by geographical borders.
As we peel back the layers of centuries, we’ll discover how English absorbed elements from the Vikings, the Normans, and beyond, turning it into the linguistic mosaic we know today. We’ll explore how historical events, technological leaps, and cultural exchanges have imprinted upon its vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation.
Join us as we unravel the layers of history, explore the confluence of cultures, and celebrate the resilience and adaptability that have made English the vibrant and diverse language it is today!
Origins of English
The roots of English stretch back to a time of great change in Britain, in the wake of the Roman Empire’s retreat in the 5th century.
After the Roman Empire withdrew its control from Britain in the early 5th century, the power vacuum left behind was filled by various Germanic tribes from what are now Denmark and northern Germany. These tribes included the Angles, Saxons, and Jutes, among others.
As they settled in Britain, they gradually displaced the Celtic and Romano-British cultures that had previously dominated the region. The Celtic speakers were pushed into peripheral areas that are now known as Wales, Scotland, and Cornwall, while the area that would become England saw the rise of a Germanic cultural and linguistic influence.
The Germanic peoples in Britain, though initially distinct tribes, eventually developed a shared cultural identity as Anglo-Saxons. This identity was not just cultural but also linguistic, as they spoke what we now refer to as Old English!
Old English
Old English was significantly different from the modern English we speak today, to the extent that it would be largely incomprehensible to contemporary English speakers!
Due to its significant differences, Old English texts and speech are largely incomprehensible to someone who only knows modern English. Without specialized study, understanding Old English would be next to impossible!
But here’s the cool part: even though Old English can seem like a puzzle to us modern English speakers, some of the most basic words we use every day are like little time travelers from that era. Words like ‘water,’ ‘child,’ ‘ear,’ ‘talk,’ and even the tiny but mighty ‘the’ have stuck with us, weaving through time to remain part of our everyday chat!
Isn’t it fascinating to think that the foundation of the language we use to text, talk, and tweet has been around for centuries, adapting and growing but still holding onto bits of its ancient roots?
Diving into Old English isn’t just about decoding old texts; it’s like unlocking the secrets of the past. It gives us a glimpse into the lives, thoughts, and stories of the Anglo-Saxons, offering a richer understanding of the origin of the English language and how it influenced the world!
Viking Influence
Starting in the 8th century, Norsemen from what are now Norway and Denmark began raiding and eventually settling in parts of England. Their presence was particularly strong in the north and east of England, an area that came to be known as the Danelaw, where Norse law prevailed over Anglo-Saxon law.
One of the most noticeable impacts of the Viking presence in England was the introduction of Old Norse words into the English language. Many of these words were absorbed into everyday language and are still in use today. Examples include ‘sky,’ ‘bag,’ ‘law,’ and ‘hit.’ The pronoun ‘they,’ along with its objective and possessive forms ‘them’ and ‘their,’ also comes from Old Norse, filling a gap in the Old English pronoun system.
But the Viking influence didn’t stop at vocabulary; it seeped into the very structure of English, nudging grammar and syntax in new directions. Some language experts think that the way English grammar got simpler, like shedding some of its complex endings and settling into a more predictable word order, might have been helped along by Old Norse. This was probably because both the Vikings and the Anglo-Saxons had to find a way to talk and understand each other!
The story of the Vikings in England isn’t just one of raiding and conquering; it’s also about making a new home, working the land, and blending in with the local folks. This mix of cultures and languages meant that the Norse impact on English was not just about borrowing a few words here and there; it was a deep, lasting fusion born out of both conflict and collaboration.
Norman Conquest
In the year 1066, a big change came to England when William the Conqueror, hailing from Normandy, claimed victory at the famous Battle of Hastings. With King Harold II defeated, William took the throne, ushering in an era of Norman influence. The Normans, who were descendants of Vikings settled in what’s now France, brought over their language, Norman French, which quickly became the language of the ruling class and the court in England.
While everyday folks kept chatting in Old English, Norman French was the go-to language for anything fancy or official, like law, church matters, and royal affairs. This mix of languages at different levels of society led to a whole lot of Norman French words finding a new home in English.
A substantial number of words in modern English, especially those related to law, government, art, literature, religion, and other aspects of high culture, are of Norman French origin. Examples include “court,” “government,” “justice,” “council,” and “parliament.”
The coexistence of Norman French and Old English led to a situation where two words with similar meanings existed in English, one of Germanic origin and the other of Romance origin. This blend has given English its rich and varied vocabulary, making it the wonderfully diverse language we speak today!
Middle English
The blending of Old English with Norman French gave rise to Middle English, the language of Chaucer and the Canterbury Tales. Middle English was more syntactically flexible than Old English and incorporated a significant amount of French vocabulary.
The English language is known for having many synonyms with nuanced differences, often tracing back to this period. For example, the English words for animals (like “cow,” “sheep,” and “pig”) are of Anglo-Saxon origin, while the words for the meats derived from these animals (“beef,” “mutton,” “pork”) come from Norman French, reflecting the roles of the English-speaking peasantry and the French-speaking nobility.
The grammar of Middle English became simpler compared to Old English, with a reduction in the use of inflections for case, gender, and number. The word order became more fixed, moving towards the Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) structure prevalent in modern English.
And just like accents and local slang can vary a lot today, Middle English had its own set of regional dialects. These varied from one part of England to another, influenced by how strongly the Norman presence was felt in the area. Some of the dialects you might have heard of include the West Midlands and East Midlands dialects, with the latter paving the way for what would eventually become the standard dialect in London and beyond.
The Great Vowel Shift
Get ready for a twist in our language tale: the Great Vowel Shift, a major makeover in English pronunciation that unfolded from the 15th to the 17th century. This big change helped usher in Early Modern English, giving our vowels a new vibe that’s stuck with us ever since!
Before the shift, the pronunciation of these vowels was more similar to their counterparts in other European languages. During the shift, the long vowels were raised, and in many cases, diphthongized (i.e., turned into a sound that combines two vowel sounds within the same syllable).
Take the word “time,” which used to sound like “teem,” or “house,” once pronounced more like “hoos.” After the shift, they moved to the pronunciations we’re familiar with today!
The exact causes of the Great Vowel Shift are still debated among linguists. Some theories suggest it was influenced by social, historical, and technological changes, including the increased mobility of the population, the mixing of dialects, and the standardization of English following the introduction of the printing press.
The shift did not occur uniformly or simultaneously across all regions of England or among all speakers. It was a gradual process that varied in pace and extent from one region to another and among different social classes.
One of the lasting impacts of the Great Vowel Shift is the discrepancy between English spelling and pronunciation. Because the shift occurred after the establishment of a standardized written form of English, many words retained their Middle English spellings even as their pronunciations changed. This is why English spelling can be so tricky!
Early Modern English
Early Modern English refers to the stage of the English language from the late 15th century to the mid-to-late 17th century. This period is marked by significant linguistic, cultural, and social changes that further shaped the English language into a form more recognizable to contemporary speakers.
This era picked up right where the Great Vowel Shift left off, changing how long vowels sounded and stirring up the relationship between spelling and how words are pronounced.
Enter William Caxton, with his groundbreaking introduction of the printing press to England in 1476. This invention was a game-changer, helping to nail down more consistent spelling and grammar rules, pushing English from its Middle stage into the Early Modern one.
This period saw efforts to standardize English grammar and spelling, partly facilitated by the printing press and the increasing availability of printed materials, including dictionaries and grammars.
Early Modern English experienced significant growth in vocabulary, due in part to the Renaissance’s influence, which led to the borrowing of words from Latin, Greek, and other European languages. This period also saw the creation of new words to describe discoveries, inventions, and concepts in science, philosophy, and the arts.
Grammar and sentence structures also got a makeover, becoming more like the English we know today. Sentences grew more complex, and auxiliary verbs started to play a bigger role, all to fit the expanding need to express increasingly complex ideas.
And who could talk about this period without tipping their hat to William Shakespeare? His creative genius in playing with words, crafting sentences, and bending poetic forms didn’t just entertain; it enriched the English language, leaving a legacy that writers, speakers, and thinkers still draw on centuries later!
The British Empire and the Industrial Revolution
The British Empire and the Industrial Revolution were two pivotal developments that had profound impacts on the English language, expanding its global reach and introducing new vocabulary and linguistic diversity
At its height in the 19th and early 20th centuries, the British Empire was the largest empire in history, encompassing territories on every continent. This global presence facilitated the spread of English as a lingua franca for administration, trade, and education in the colonies.
As English spread through the empire, it absorbed words and phrases from a multitude of languages, enriching its vocabulary. Words from Indian languages like “bungalow” (from Bengali বাংলা/bangla), “shampoo” (from Hindi चाँपो/chāmpo), and “jungle” (from Hindi जंगल/jangal) were incorporated into English.
The spread of English led to the development of distinct regional dialects and varieties, such as Indian English, Australian English, and Caribbean English, each with its own unique pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar.
Then came the Industrial Revolution, starting in Britain and spreading like wildfire. It wasn’t just machines and smokestacks; it was a revolution in words too. Suddenly, we needed to talk about “engines,” “railways,” and “factories.” New inventions and ways of living brought new words into our everyday chats and changed some we already had.
This era of change didn’t just boost our vocabulary; it transformed society, making cities the new hubs of life and turning reading and writing from elite skills to everyday necessities. Newspapers, novels, and manuals spread like never before, taking English along for the ride and helping to standardize it in the process.
Together, the British Empire’s global footprint and the Industrial Revolution’s innovations didn’t just spread English; they transformed it, setting the stage for its role as the world’s go-to language for international chat, from business to science to pop culture!
Modern English
The 20th century was an amazing time for technology, bringing us game-changers like radio, TV, and, of course, the internet. These innovations weren’t just cool gadgets; they helped spread English all over the world, making it more common and understood by people everywhere.
During this time, the United States grew in power and influence, especially after World War II. This rise made American English very popular worldwide, especially through movies, music, and technology.
As the world got more connected, English became the go-to language for international talks, business, and even online. This led to what some people call “Global English” or “International English.” This kind of English is all about making sure people from different places can understand each other, even if they have different mother tongues.
In some places, English mixed with local languages, creating new types of English. For example, in Singapore, there’s something called “Singlish,” which blends English with Malay, Tamil, and Chinese dialects. It started simple but grew into a unique way of speaking that’s a big part of life in Singapore.
So, modern English isn’t just one thing; it’s a mix of influences and ideas from all over, constantly changing and growing as it connects people across the globe!
Summary
And that’s it, folks!
Thank you for joining me on this journey. May your adventures with the English language be as rich and rewarding as the history it carries.
Summary
And there you have it! Seven tips to help you get better at English speaking!
Remember, the journey to fluency is a mix of courage, practice, and smart strategies. Embrace your unique voice, immerse yourself in the language, and always keep the communication doors open.
Most importantly, enjoy the process and the incredible growth that comes with it!
Whether you’re chatting with a friend, presenting in a meeting, or just practicing in front of a mirror, every word you speak is a step closer to mastery. So go ahead, make those mistakes, try out those new phrases, and let your confidence soar. You’ve got this!
Happy learning and keep on speaking!
At IELC, we teach English the right way
Our goal is to get you speaking in English with fluency and confidence as fast as possible. We want to give you the skills you need to fulfil your potential!
Our experienced teachers will guide you along every step of the learning process to ensure that you are not wasting your time, money, and energy on useless language exercises & wrong methods.
Our courses
With our modern campus and technology, we are equipped to provide the best possible courses for children, teens, and adults, including:
Online and on campus IELTS courses
Online and on campus TOEFL PBT courses
Online and on campus TOEFL iBT courses
We offer our classes in group classes or private classes.
No matter what your goals are, our team will help you achieve these goals by providing you with Indonesia’s best English courses!
Talk to our team today to get your FREE consultation and take your first step towards success.
Sincerely,
IELC Academic Director
