
Mastering phrasal verbs: practical guide, examples, and quiz
Welcome back, learners!
Let’s talk about something that tends to give English learners a bit of a headache – yes, you guessed it right, phrasal verbs!
Do you find phrasal verbs a bit…baffling? Maybe they seem like an unsolvable puzzle, each one with its own unique, sometimes perplexing, rules.
Well, you’re certainly not alone!
Many people find these tricky little combinations of verbs and prepositions to be one of the more challenging parts of mastering English.
But don’t fret, we’re here today to take some of the mystery out of these puzzling phrases.
In this blog post, we’re going to decode phrasal verbs and put them into simple, understandable contexts. We will uncover the logic behind these structures, provide you with practical learning strategies, and make them less intimidating. You’ll learn how to not just understand them, but use them with ease and confidence!
Without further ado, let’s get started!
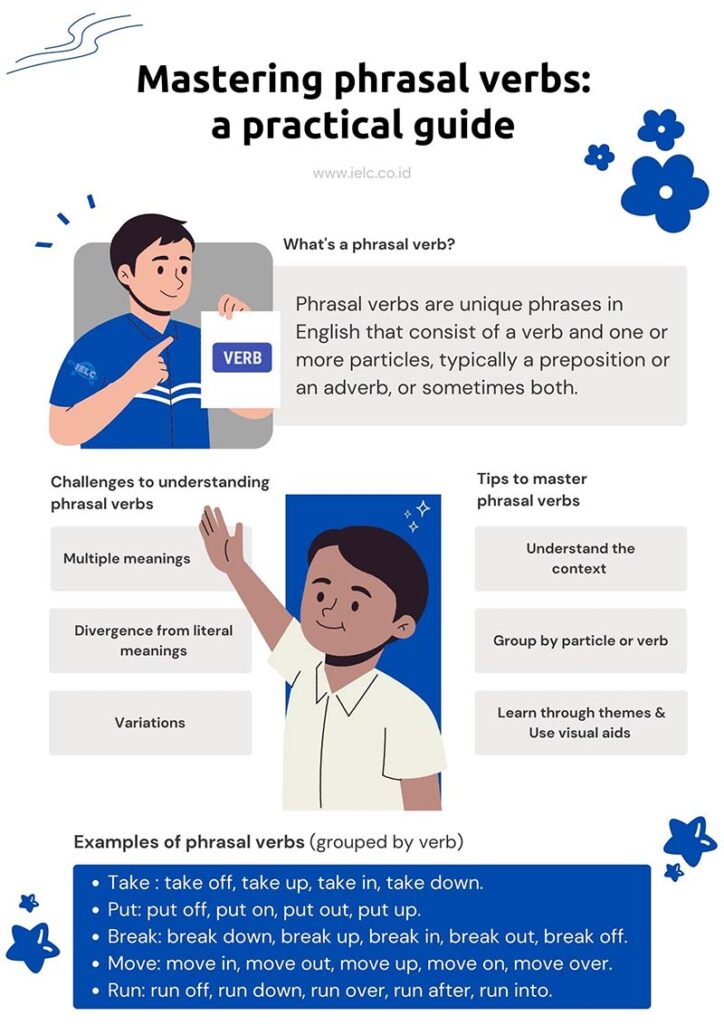
What is a phrasal verb?
Phrasal verbs are unique phrases in English that consist of a verb and one or more particles, typically a preposition or an adverb, or sometimes both.
Simply put, It’s a little group of words that includes a verb and words like “on”, “up”, “out”, or “in”. When these words are used together, they usually have a different meaning than the verb by itself.
Let’s use “turn” as an example. “Turn” usually means to move in a circle. But if you add different small words to it, it can mean different things:
- Turn on: This means to start something, like a light or a computer.
Example: Can you turn on the light, please?
- Turn off: This means to stop something from working, like a TV or a radio.
Example: Please turn off the TV when you’re done!
- Turn up: This can mean to increase the volume of something.
Example: Can you turn up the music? I love this song!
- Turn down: This means to lower the volume
Example: It’s too loud in here! Can you turn down the music?
- Turn down: To decline or refuse an offer or invitation
Example: My boss offered me a promotion, but I had to turn it down because it required moving to another city.
So, even though “turn” has one meaning by itself, it can mean many different things when it’s used with other prepositions. This is what makes phrasal verbs special. They can be a little tricky, but once you start to understand them, they can help you express lots of different ideas in English!
Interestingly, even the same phrase, such as “turn down” can have multiple meanings, as shown above. Understanding these different meanings is a key aspect of mastering phrasal verbs!
Understanding phrasal verb: the challenges
Phrasal verbs, though an integral part of English, are often a source of confusion for English learners, and there are a few reasons for this:
- Multiple meanings
Some phrasal verbs can have many different meanings. Take “break down” for example. It could mean that a machine has stopped working, as in “my car broke down” or it could mean to emotionally collapse, as in “he broke down in tears” or even to divide something into smaller parts, as in “let’s break down the problem”. The fact that the same phrase can mean different things can make phrasal verbs confusing.
- Divergence from literal meanings
Even when the individual words in a phrasal verb are familiar, their combined meaning in a phrasal verb can be quite different. “Look,” “for,”, and “up to” all have simple, straightforward meanings on their own, but “look up to” as a phrasal verb means to admire or respect someone. This difference between the literal and phrasal meaning can be confusing.
- Variations
Some phrasal verbs can be separated by other words, while others cannot. For example, you can say “turn the TV off” or “turn off the TV”, but you can only say “run into a friend” not “run a friend into”. This inconsistency in structure adds another layer of complexity.
Tips to master phrasal verbs
- Understand the context
One of the most effective ways to understand phrasal verbs is through context. Each time you come across a new phrasal verb, observe the situation in which it’s used. This will give you clues about its meaning and how to use it appropriately. Over time, as you encounter the same phrasal verb in different contexts, you’ll develop a more nuanced understanding of its usage and meaning.
- Group by particle or verb
Another helpful strategy is to learn phrasal verbs in groups. You could group them by a common particle, such as “up”, “down”, “in”, “out”, etc., or by a shared verb. For instance, learning “turn up”, “turn down”, “turn in”, and “turn out” together can make it easier to remember their meanings, as they are linked by the common verb “turn”.
- Learn through themes
Phrasal verbs can also be learned through themes or topics, such as travel, work, or health. For example, if you’re learning travel-related vocabulary, you might focus on phrasal verbs like “check in”, “set off”, “take off”, and “pick up”. This way, the thematic connections can help you recall the appropriate phrasal verbs when you’re discussing that topic.
- Use visual aids
Visual aids like flashcards or diagrams can be excellent tools for learning phrasal verbs. Write the phrasal verb on one side of the flashcard, and its meaning and an example sentence on the other. You can also create diagrams or mind maps grouping phrasal verbs by their shared verb or particle, or by theme. These visual representations can help solidify your understanding and recall of phrasal verbs.
Mastering phrasal verbs is a challenge that requires consistent effort and practice. But with these strategies, along with regular exposure to English in real-world contexts, you’ll find yourself gradually becoming more comfortable with phrasal verbs!
Examples of phrasal verbs (grouped by verb)
1. Take
► Take off
To depart, usually in relation to air travel or to become successful or popular very quickly.
Example
- The plane is scheduled to take off at 3 PM.
- Her fame really took off after she starred in that Netflix series.
► Take up
To start a new hobby or activity.
Example
- She decided to take up painting to relax.
► Take in
To absorb or understand information or to provide someone with a place to stay.
Example
- I couldn’t take in all the information from the lecture.
- When my cousin lost his job, we decided to take him in until he could get back on his feet.
► Take down
To dismantle or disassemble something or to defeat or overpower someone, often in a competition or fight or to write or record information
Example :
- After the birthday party, we had to take down the decorations.
- In the final round of the chess tournament, the underdog managed to take down the reigning champion.
- Can you take down the minutes of the meeting?
2. Put
► Put off
To postpone or delay
Example :
- We had to put off our meeting until next week.
► Put on
To dress oneself in clothing or to gain weight or to feign certain emotion or mannerism.
Example
- She put on her jacket before leaving the house.
- He has put on a few kilograms after the holiday.
- She put on a brave face in front of her children, but she was worried.
► Put out
To extinguish something that’s burning or to produce or publish something.
Example :
- Firefighters put out the fire in the building.
- The author puts out a new book every year.
► Put up
To build something, often something temporary or to tolerate or endure something or someone or to offer resistance.
Example
- We put up a tent for the camping trip.
- I can’t put up with his rude behavior any longer.
- Despite being outnumbered, they put up a good fight.
3. Break
► Break down
To stop functioning (often used for machinery or vehicles) or to lose control of one’s emotions, often crying.
Example
- My car broke down on the highway, and I had to call for a tow truck.
- When she heard the news, she broke down in tears.
► Break up
To end a relationship.
Example
- They decided to break up due to irreconcilable differences.
► Break in
To forcibly enter a place, especially a building or to interrupt someone.
Example
- Someone broke in while we were on vacation and stole our TV.
- I hate to break in, but I have some relevant news to share.
► Break out
To suddenly start, usually used for wars, fights, or diseases or to escape from prison or to suddenly develop a skin condition like a rash or acne.
Example
- When the epidemic broke out, the government immediately took action.
- Two prisoners broke out last night, and the police are still searching for them.
- I always break out in pimples when I’m stressed.
► Break off
To end something abruptly, like a relationship or discussion or to become detached or separated from a larger piece.
Example
- They decided to break off their engagement due to irreconcilable differences.
- A large chunk of ice broke off from the glacier.
4. Move
► Move in
To start living in a new residence.
Example
- She will move in to her new apartment next week.
► Move out
To leave your current residence and start living somewhere else.
Example
- He finally decided to move out of his parents house.
► Move up
To advance, improve position, or be promoted.
Example
- She started as an entry level employee but quickly moved up to the managerial position.
► Move on
To stop doing or focusing on something and start doing something else or to emotionally let go of a past situation or relationship.
- After spending a month on this project, it’s time to move on to the next one.
- He had a tough break-up, but he’s decided it’s time to move on.
► Move over
To shift one’s position to make space for someone else or to give way to someone, often in terms of a job.
Example
- Move over, I need to sit down!
- It’s time for the CEO to move over and let someone else take charge.
5. Run
► Run off
To leave quickly or to run away.
Example :
- The thieves ran off when they heard the police sirens.
► Run on
To continue without stopping; in speaking, to talk for a long time without pausing.
Example
- She’s known to run on about her travels for hours.
► Run down
To hit someone or something with a vehicle or to criticize someone or something harshly or to lose power or stop functioning (usually in relation to battery machinery) or referring to an old, dilapidated place; in a state of disrepair.
Example
- He was run down by a bus while crossing the road.
- He’s always running down his colleagues.
- My phone’s battery has run down. I need to recharge it.
- The old farm was so run down that it was almost uninhabitable.
► Run over
To hit with a vehicle or to review or rehearse something.
Example
- He didn’t see the sign and ran over it.
- Let’s run over the plan one more time.
► Run after
To chase or pursue someone or something.
Example :
- He ran after the bus but it was too late.
► Run into
To meet someone unexpectedly.
- I ran into Steve on my way out.
Remember, context is key to determining which meaning of a phrasal verb is intended. Keep practicing and interacting with English in varied contexts, and you’ll get a better grasp of these versatile phrases!
Now, let’s test your knowledge!
Phrasal verbs quiz
1. I’m tired, I think I’ll ________ early tonight.
a) turn up
b) turn out
c) turn in
d) turn over
2. She needs to ________ her strength before the big game tomorrow.
a) build up
b) build in
c) build on
d) build over
3. The two companies decided to ________ rather than compete against each other.
a) join in
b) join on
c) join up
d) join over
4. We will ________ our plan at tomorrow’s meeting.
a) run over
b) run off
c) run on
d) run out
5. He decided to ________ smoking for his health.
a) give up
b) give in
c) give on
d) give over
6. I need to ________ on my work before the deadline.
a) catch up
b) catch in
c) catch on
d) catch over
7. The car ________ in the middle of the road.
a) broke down
b) broke up
c) broke in
d) broke on
8. They ________ their differences and became friends.
a) put aside
b) put up
c) put down
d) put on
9. I always ________ my promises.
a) live on to
b) live in to
c) live down to
d) live up to
10. She decided to ________ her English skills.
a) brush in on
b) brush up on
c) brush down on
d) brush over on
Answer key
- C) Turn in
- A) Build up
- C) Join up
- A) Run over
- A) Give up
- A) Catch up
- A) Broke down
- A) Put aside
- D) Live up to
- B) Brush up on
Next steps
Do you want to speak English with confidence?
Most people lack confidence when they speak English. They are afraid to make mistakes and are embarrassed to speak in front of others.
This is because they have been taught English the wrong way!
Most English courses waste your time and money on useless exercises that don’t bring results. Even worse, they teach you bad habits that are very difficult to unlearn.
As a result, you become confused and lack confidence. This is wrong!
At IELC, we teach English the right way
Our goal is to get you speaking in English with fluency and confidence as fast as possible. We want to give you the skills you need to fulfil your potential!
Our experienced teachers will guide you along every step of the learning process to ensure that you are not wasting your time, money, and energy on useless language exercises & wrong methods.
Our courses
With our modern campus and technology, we are equipped to provide the best possible courses for children, teens, and adults, including:
We offer our classes in group classes or private classes.
No matter what your goals are, our team will help you achieve these goals by providing you with Indonesia’s best English courses!
Talk to our team today to get your FREE consultation and take your first step towards success.
Sincerely,
IELC Academic Director
